CET324 (Advanced C.S) PPW1 Task and Submission
- Details
- Category: Level 3, Advanced Cyber Security
- Published: Wednesday, 03 February 2021 19:14
- Hits: 1314
Task
CET324 – Advanced CyberSecurity
The following learning outcomes will be assessed:
Knowledge
Critical understanding of the principles and applications of cybersecurity, societal, legal and business issues involved in secure systems taking into account the potential security threats, breaches, risks and attacks
Skills
Analysis and evaluation of the professional requirements of a cybersecurity practitioner, and critically discuss the challenges facing the cybersecurity practitioners as an individuals and as part of organisations.
Important Information
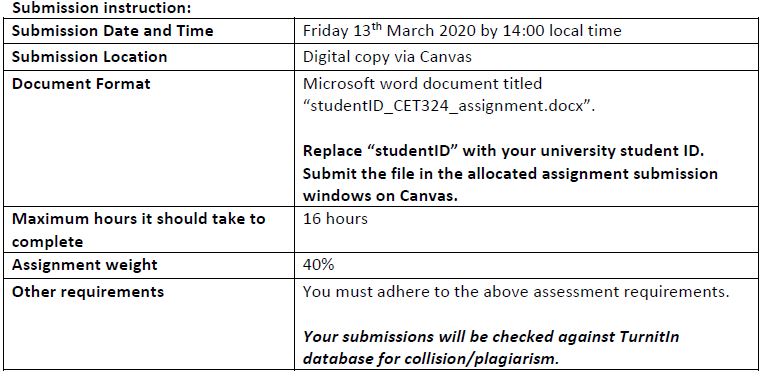
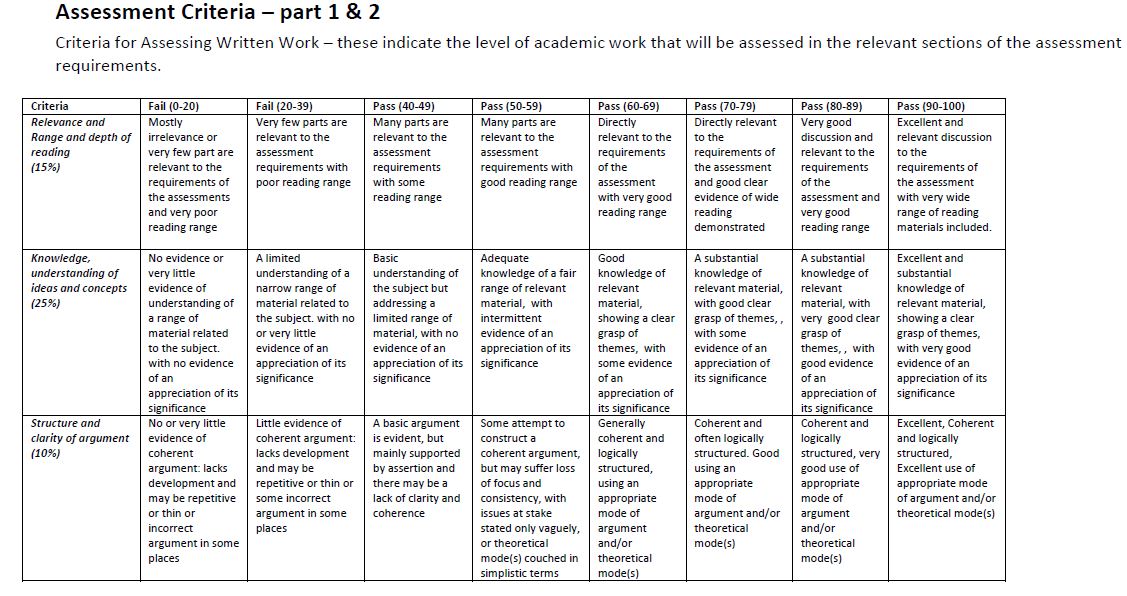
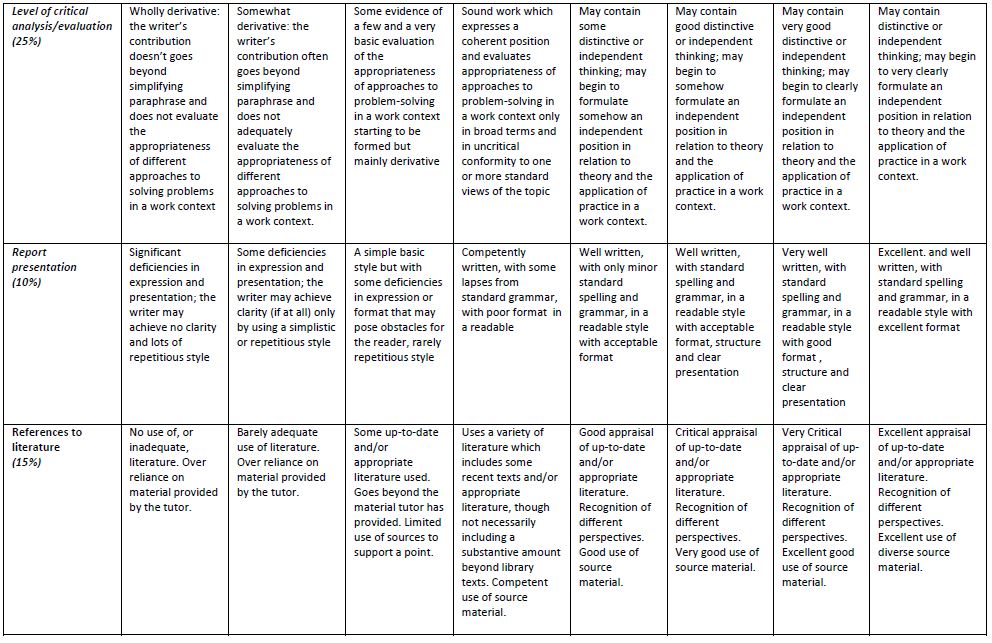
You are required to submit your work within the bounds of the University Infringement of Assessment Regulations (see your Programme Guide). Plagiarism, paraphrasing and downloading large amounts of information from external sources, will not be tolerated and will be dealt with severely. Although you should make full use of any source material, which would normally be an occasional sentence and/or paragraph (referenced) followed by your own critical analysis/evaluation. You will receive no marks for work that is not your own. Your work may be subject to checks for originality which can include use of an electronic plagiarism detection service.
For this assessment you are asked to submit an individual piece of work, therefore the work must be entirely your own. The safety of your assessments is your responsibility. You must not permit another student access to your work.
Referencing for this assessment should be done using the Harvard referencing system. (see your Programme Guide).
Please ensure that you retain a duplicate of your assignment. We are required to send samples of student work to the external examiners for moderation purposes. It will also safeguard in the unlikely event of your work going astray.
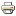
Allocated time:
Students with no support plan: Deadline is Friday 13th March at 14:00.Students with support plan: Deadline is Friday 13th March at 16:30. If any student in this category require more than 3 hours extension should discuss the requirement with the module leader before the deadline.
Assignment Specification
Section A
Produce a report consisting of the following two parts.
Part 1 (45 marks)
The cybersecurity environment is a wide and complex one. For this part of the assignment you are required to produce a report (approximately 1500 words) outlining the minor and major threats that a) individuals in society and b) organisations face from threats and breaches of cybersecurity. Your report should include a discussion on the probability of the threats and breaches happening, where they are likely to come from, their impact and their resultant consequences on the victims.
You should support your analyses, arguments, evidence and finding by scholarly works through literature research.
Part 2 (55 marks)
Based on the work that you have undertaken on this module – both in seminar/lab tasks and in independent study, produce a report (approximately 1750 words) to identify the steps (before and after attack) that can be taken by individuals and organisations to enhance their cybersecurity systems/environments. Your report should describe the steps that can be taken, the cybersecurity actions that such steps will provide and an evaluation of the effectiveness of the steps to individuals and organisations.
You should support your analyses, arguments, evidence and finding by scholarly works through literature research.
Submission
CET324 – Advanced CyberSecurity
Assignment 1
Report
Student Name: Andrea Eva Frankone Balazs
Registration Number:
Programme: BSc (Hons) Web and Mobile Development
Part 1
Threats, breaches and their probabilities
Security threats and breaches aim to exploit the vulnerabilities of a system. Both the organisations and the individuals face the same kind of threats and breaches, such as; advanced persistent threats, identity or other information thefts, distributed denial of service, denial of service attacks, spear phishing, data exfiltration, etc. However, organisations can be more vulnerable to these attacks and have the potential to cause more damage to the organisation that it would be to an individual, as organisations can have a lot more sensitive information stored on their systems and databases than an individual would on their computer. For example organisations can store the personal data of a substantial amount of people with this data consisting of card numbers, names, addresses, emails, names, passwords, D.O.Bs, etc. Over all, if an individual's computer were to be attacked, they would only lose their information which compared to an organisation losing hundreds of peoples’ information. There are different levels of impact, which is the impact and the consequences of the attack that it has on the operation and assets of an organisation and on individuals. Firstly the low impact, which has a very low or limited adverse effect on the individual or organisation. Then there is the moderate level which is that the impact could have a very serious impact on the targeted individual or organisation. Then finally the high level, which could have a catastrophic effect on the individual and the organisation.
The following survey compared their findings of cyber security breaches from 2017 to 2019.
“Around a third (32%) of businesses and two in ten charities (22%) report having cyber security breaches or attacks in the last 12 months. As in previous years, this is much higher specifically among medium businesses (60%), large businesses (61%) and high-income charities (52%).2 “(Vaidya, R., 2019.)
However, this survey and many other articles don't consider the threats to individuals only organisations and charities, these two, individuals and organisations, are never discussed together in any report or survey.
Cyber attacks are a fast growing and increasing crime in the world as computers and technology is developing at a rapidly increasing rate, this gives more opportunities and weaknesses for attackers to exploit. The second largest major data breach was suffered by Marriot near the end of 2018, it “is estimated to have exposed 500 million user accounts.”(Morgan, S., 2019.)
There were no articles found on the probability or statistics for the threats to individuals, however we found multiple surveys on statistics of the impact of the organisation being attacked also impacting individual’s information and data being breached at the same time.
This shows that whenever organisations are under attack this attack can also impact the individuals that have trusted the organisation with their personal data.
Types of hackers
There are many different types of hackers out there, firstly the script kiddies, these tend to be younger people who use existing computer scripts and codes to hack into computers, these aren't experienced or expert hackers as they lack the expertise. Other types of hackers are white hats, these are people like pentesters who as a profession are hired by organisations so that the pentester can hack and find the organisations weaknesses, but this is all done within the rights that the pentester was given permission and access to by the company. Then there are the grey hats who may violate laws and perform illegal actions, but they don’t have malicious intent like black hats do who violate laws for personal gain or malicious intent, grey hats might do something by accident without knowing what they are doing is illegal or wrong. Finally, there are suicide hackers, whos only intent is to create chaos and destruction for the reason of revenge. Hackers also include organisations or groups of hackers, who develop and execute the attack codes.
The following article analysed and explored the emerging and existing tools that hackers are using for malicious intent and to hack organisations or even individuals “Cyber attacks, or the deliberate exploitation of computer systems through the use of malicious tools and techniques such as Ransomware, Zeus Trojans, and Keyloggers, cost the global economy approximately $445 billion per year”(Samtani, S. et al. 2017). There are also some other types of attacks out there, one of the most popular being social engineering, where the hacker or attacker communicates directly to a user to try and collect important data, for example phishing where the attacker sends the victim an email with a malicious link with viruses or other attacks and they try to trap the victim into clicking onto the link. There are also passive and active attacks. Passive attacks make use of information from the system without affecting the system resources, this can include monitoring a computers activities or a user's activities, mostly through traffic analysis their main goal is to find information without getting caught. Whereas, active attacks actually try to modify the systems resource to try and affect the way they operate, this includes the creation or alteration of data streams. All of the above are also all examples of not only attacks but breaches and threats to organisations and individuals.
There is a typical hacking process that both white and black hats use, it begins with footprinting, which is a technique used for gathering information about the computer and the user and mostly the organisation too if that's the target. Next is the scanning, which is used to scan and identify live hosts, ports, services, operating systems and architecture. This is so when they find the operating system that the user uses and the version, then they will know what that version’s weaknesses are and exploit them. Then it is enumeration, which is where they uncover all of the information that they have found during the scanning stage, after that it is the system hacking stage where you take the information and attack the system. Then the hacker would move onto the escalation of privilege, where they gain more privileges to be able to gain access to more sensitive information or gain more control to the system. Finally it is the covering their tracks stage and then planting backdoors if they are able to gain access to the system again more easily.
Impact and consequences on the victims
The following article discussed and reviewed the trends, scale and nature of economic cybercrimes, where they found that in the UK “The large majority of victims of fraud had been a victim only once (84 %), although repeat victimisation (within the same 12 month crime reference period) was more common among victims of bank and credit account fraud (14 %) than among victims of other types of fraud.” (Levi, M. 2017)
There are also social and psychological effects to the victims of cybercrime, when people talk about cybercrime they mostly just mention data breaches and theft of personal and sensitive information, but it also can have big impacts on society, for example in the following article they researched the social and psychological impact of cyber-attacks ”One example of this is a cyber-attack where malware infects a national power station causing the hundreds of thousands of citizens to be without power.”(Bada, M. and Nurse, J., 2019.) This shows the impact that cybercrime truly can have on individuals and organisations, as recovery after a cyber-attack is a long and costly process. “Cyber attacks cost the global economy approximately $445 billion per year.” (Samtani, S. et al. 2017)
It can also have emotional impacts such as, “the person becoming distressed and be left feeling violated, betrayed, vulnerable, angry and powerless” (Kirwan and Power, 2011). This could potentially lead to the individual not trusting organisations and into wanting to stay away from the computer, as there are cyber attacks when a individual’s content is stolen like images, files, etc and the attacker asks for money in return for them to get their information back and if they don’t pay the amount the files will be deleted.
This can also deter the older generation or less knowledgeable people about computers from using computers incase of any cyber-attacks. “Findings show that less than 1 in 10 people (9%) claim that they feel ‘very’ safe online. Also, only half (51%) of adults asked, would change the way they behave online if they became a victim” (Symantec, 2010).
This shows that many people don’t think security is a big issue and they dont take steps towards making their computer more secure against attacks, which could also impact the organisation that they work for, if they don't know how to securely use their home computers and aren't aware of the threats and attacks that can take place, these could subsequently impact the organisation that they work at as they wouldn't be aware of these, which in turn could lead to more attacks and more people potentially impacted by this attack. Over all the aims of security should be confidentiality, which is that the data is to be defended against unauthorised personnel, then there is availability which is the extent of access that is provided to the user for the user to be able to use for the needed purposes. Then finally integrity, which is making sure that the data can be modified and only be the mechanisms that allow access to those privileges.
Part 2
Steps to enhance cybersecurity systems
When it comes to cybersecurity in organisations, you have to ensure that there have been clear processes and procedures in place to detail the security domain, which include breaches, threats and risks that could potentially harm the organisation. There should also be a procedure in place for the detection of when a breach of security has taken place, these should incorporate spotting certain issues with policy, maybe the policy is out of date or needs to be updated whenever the system is also updated and the application of these policies. There will also need to be processes put in place to define what can be done to defend the organisation or an individual of any potential attacks or threats they might be faced with. Finally, there should be procedures put in place to be able to deter potential hackers and attackers from trying to penetrate the organisations system.
One of the key aspects that is needed in an organisation when it comes to cybersecurity would be making sure that all the staff receive adequate training and have a large awareness of all the cyber threats and potential threats out there. However, “analysis revealed that individual human actors, in a variety of roles, are generally considered to be “a problem”.” (Zimmermann, V. and Renaud, K. 2019) This article discusses how the employees tend to be viewed as the “problem”, because the organisation and government they work for takes away the human aspects of them by making them follow these rules and policies, because the organisation expects them to be the ones to do something malicious against the organisation, therefore the organisation tries to restrict them as much as they possibly can with rules. They wanted a “cybersecurity, differently” approach where the employees were allowed my freedom and flexibility and more chances to expand on their knowledge, so that in turn they would be able to learn from their mistakes or whenever they achieve something. However, they stated that more research will be needed on this topic as till now they haven't put this theory into affect or applied it anywhere as of yet.
A report that was found conducted a survey in 2016 which investigated how the fast development of technology has changed their members’ views on cybersecurity. Where ”Only 57% said they had a formal cyber/information security strategy”(Sproule, J., 2016.) 49% had said that they had provided cyber awareness training to their staff, then 6% had stated they had spent nothing in the last year on cyber security.
Stage 1 of securing any network would be to secure it, to apply defences against threats, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems and also vulnerability patching of all the software systems. Another good security measure would be a connection with a VPN, virtual private network, which protects information that is being sent across private networks and lower security areas of private networks. Finally ensuring user trust and identity, meaning authentication and authorisation of all the accounts on the system and applying user policies, which would be extremely helpful to organisations.
Stage 2 is monitoring, the security system that has been put in place to ensure that it is working effectively, how it impacts the network performance, that it still abides by the set out security policies, should also use IDS, intrusion detection systems, to ensure that if there is breach or an attempt at a breach the system detects it correctly and finally to ensure that the auditing is actually taking place. All this monitoring should be implemented in real-time to make sure that it is working confidently.
Stage 3 is testing, this is when tools are equipped to test the security system, assessment tools used to test for weaknesses such as Nessus, Nmap, etc.These testings need to take place at both the network and host levels of the network periodically, ethical hackers can be employed to test these.
The final stage is stage 4 which is the improving stage, after the ethical hacker has been employed to test the security of the network, there should be adjustments made to improve upon any weaknesses that the network presented, these adjustments should also be made when there are changes made to the policies. These stages should be repeated as all the new threats continue to develop and evolve so should the security of the network.
The cybersecurity these actions provide
In stage 1 there was mentions of a firewall, a firewall is a barrier of sorts that monitors the incoming and outgoing network traffic, which are based on the security rules and policies it was given and set to. An intrusion detection system is a software that monitors the system for any detection of an malicious activity that might be going on in the system. Then there is a virtual private network, which allows an individual to produce a secure connection to other networks over the internet, these can be used to provide security from “unsecured public Wi-Fi, from prying eyes, hackers or data thieves.”(Big Brother Watch, 2017)
Authentication of a user is there to make sure that the user is who they claim they are, that they are the correct person, then authorisation is the part that allows the user to access different sorts of resources that are based upon the needs of the user, what the user needs to be able to perform their needed tasks and jobs. Authentication of a user should be private, reliable, and confirms who the user claims to be. There are different ways authentication can be done, it can be something that the person knows, so a password or a pin number. It can also be something that the person has or possesses, such as a keycard or a smartcard, it can also be something that the person is, meaning biometrics, so fingerprint, retinal and face scans. Then finally there is something that the person does, which can be a voice pattern, handwriting or the rhythm of which they type.
Then in stage 3, testing stage, there are assessment tools that can be used to check the security of the system, for example Nessus. Nessus is a scanning tool, this scan scans the computer and if there are any vulnerabilities that can be used by hackers for malicious intent then it alerts the computer to this issue. Then there is the Nmap which is also a scanner but an open-source network scanner, this is used for not only scanning and detection vulnerabilities but also for the uncovering of networks, this means it discovers hosts that are accessible and the services that provide. There is also a file integrity monitor that can be used for intrusion detection, Tripwire, which is constantly and under its own power keeps critical system files and reports under management, in case they have been modified or destroyed by either a cracker or just by mistake. Finally there is swatchdog, which is a script created for the monitoring of active log files, but only on unix-like systems, eg.Linux.
Evaluation of effectiveness of steps to enhance cybersecurity systems
Stage one of enhancing cyber security issues covers securing the computer system. The advantages to this stage is that it is a good starting point, it is the foundation of where you would start, just by introducing effective defences such as firewalls . Firewalls are effective as they are: “low cost, packet filters make use of current network routers, makes Security Transparent to End-Users, Easy to install, packet filters make use of current network routers, packet filters are generally faster than other firewall technologies because they perform fewer evaluations.”(UKEssays. November 2018 A). Also the use of intrusion prevention/detection systems is useful in the use of stage one as they are “lower cost of ownership, easier to deploy, detect network based attacks, retaining evidence, real-time detection and quick response, detection of failed attacks.” (Vijayarani, D. and Sylviaa.S, M., 2015). This shows that the first stage in enhancing cyber security systems is a very good starting place as it suggests very strong and secure options for when wanting to or starting to secure any sort of system whether it be for an individual for a small network or for a large organisation that's dealing with a larger network setup, it is a good starting point for someone who might know a little bit about cybersecurity. However, there should be a stage before this one where it informs and help people who are clueless about cybersecurity to gain some understanding on what it is and why is it so important, especially businesses as some businesses do tend to look past some security issues so a small introduction stage would be better instead of jumping straight into the securing of the system, because if a person with very little understanding of the topic might get intimidated by the number of things that they are being asked to do, the stages could be a little more detailed in terms of the steps, but for more expert people in this area that might be irritating.
Stage two, is a good way to follow up after stage one is completed, however it is a big leap from securing the system to monitoring it, especially if it is a big network then it would need some considerable time before it could move onto monitoring the system. Another disadvantage of stage two would be that it can be time consuming and costly to keep monitoring the system, also stage two does not state what to do when you can not surpass stage two, because what if one of the systems that have been put in place does not work properly, they would have to go back to stage one and that should be stated in stage two incase someone does find them selve in that situation, for some guidance and help.
Stage three, which is the testing stage is another good stage to go to when coming out of stage two as it has many useful and and good quality tools that can be used within it, for example, Nessus. Nessus is a great tool to use as it is a free desktop-scanning product and very inexpensive if and when it is being used for commercial use, “many programmers that create plug-ins, tools and new vulnerability checks for this program because its open source and everyone can use” (UKEssays. November 2013). Then there are also the nmap scans, for example an ACK scan operation, the advantages are that with “this kind of scan where a single port is primarily scanned is unnoticeable and nearly invisible when combined with the other traffic.” (UKEssays. November 2018.S). Overall, stage three is a great stage to follow up after stage two with very useful and outstanding scans and tools that will help any individual or organisation that would turn to this stage for help.
Stage four, is an excellent stage which is all about improving and constantly updating and evolving the system with the evolving and never ending increment and development of technology it is a very important step, it is necessary to keep the system not only updated but to keep checking and testing if it is up to working order and that there are still no possibilities of any weaknesses in the system to be exploited to have a very secure system.
References
Bada, M. and Nurse, J., 2019. The Social And Psychological Impact Of Cyber-Attacks. [ebook] Available at: <https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1909/1909.13256.pdf> [Accessed 12 March 2020].
Kirwan, G. & Power, A. (2011). The Psychology of Cyber Crime: Concepts and Principles. IGI Global.
Big Brother Watch, 2017. Virtual Private Networks Privacy Factsheet. [ebook] www.bigbrotherwatch.org.uk. Available at: <https://bigbrotherwatch.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/VPN.pdf> [Accessed 12 March 2020].
Levi, M. (2017) ‘Assessing the trends, scale and nature of economic cybercrimes: overview and Issues’, Crime, Law & Social Change, 67(1), pp. 3–20. doi: 10.1007/s10611-016-9645-3.
Morgan, S., 2019. 2019 Official Annual Cybercrime Report. [ebook] Cybersecurity Ventures sponsored by Herjavec Group. Available at: <https://www.herjavecgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/CV-HG-2019-Official-Annual-Cybercrime-Report.pdf> [Accessed 12 March 2020].
Samtani, S. et al. (2017) ‘Exploring Emerging Hacker Assets and Key Hackers for Proactive Cyber Threat Intelligence’, Journal of Management Information Systems, 34(4), p. 1023. Available at: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edb&AN=127056615&site=eds-live&scope=site (Accessed: 12 March 2020).
Sproule, J., 2016. Cyber Security Underpinning The Digital Economy. [ebook] Available at: <https://www.iod.com/Portals/0/PDFs/Campaigns%20and%20Reports/Digital%20and%20Technology/Cyber%20Security%20-Underpinning%20the%20digital%20economy.pdf?ver=2016-09-13-171033-407> [Accessed 12 March 2020].
Symantec. (2010). Norton Cybercrime Report: The Human Impact. Retrieved June 14 2018, from https://www.symantec.com/content/en/us/home_homeoffice/media/pdf/cybercrime_r eport/Norton_USA-Human%20Impact-A4_Aug4-2.pdf
UKEssays. November 2013. What Are The Main Features Of Nessus Information Technology Essay. [online]. Available from: https://www.uniassignment.com/essay-samples/information-technology/what-are-the-main-features-of-nessus-information-technology-essay.php?vref=1 [Accessed 12 March 2020].
UKEssays. November 2018. Advantages And Disadvantages Of Firewalls Computer Science Essay. [online]. Available from: https://www.ukessays.com/essays/computer-science/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-firewalls-computer-science-essay.php?vref=1 [Accessed 12 March 2020].
UKEssays. November 2018. Security of a network. [online]. Available from: https://www.ukessays.com/essays/education/security-of-a-network.php?vref=1 [Accessed 12 March 2020].
Vaidya, R., 2019. Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2019. [ebook] Portsmouth. Available at: <https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/813599/Cyber_Security_Breaches_Survey_2019_-_Main_Report.pdf> [Accessed 12 March 2020].
Vijayarani, D. and Sylviaa.S, M., 2015. Intrusion Detection System - A Study. [ebook] Available at: <http://airccse.org/journal/ijsptm/papers/4115ijsptm04.pdf> [Accessed 12 March 2020].
Zimmermann, V. and Renaud, K. (2019) ‘Moving from a ‘human-as-problem” to a ‘human-as-solution” cybersecurity mindset’, International Journal of Human - Computer Studies, 131, pp. 169–187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhcs.2019.05.005.